Transforming data with the RxJS Map operator
The RxJS map() operator is one of the most used operators, it’s a powerful tool for transforming data with streams. It takes an input, transforms it and returns the transformed data.
The map() operator is often used to transform objects from one type to another, or to manipulate objects, for example adding properties or changing the values of existing properties.
In this article, we’ll discuss several examples of how to use the RxJS map() operator.
Basic usage of map()
First, we import the map operator from rxjs/operators.
import { map } from 'rxjs/operators'
Next, we define our source observable name$, which is in our case an Observable<string> that will emit the value of a string 'Angular'.
name$: Observable<string> = of('Angular);
Next, we will transform name$ to a personalized greeting with the map() operator within a pipe().
personalizedGreeting$: Observable<string> = name$.pipe(
map((name) => `Hello ${name}`)
);
The personalizedGreeting$ observable will output Hello Angular when subscribed to.
Using multiple map() operators
We can also use multiple map() operators within the same pipe() operator.
nameWithGreetingAndExclamation$: Observable<string> = of('Angular').pipe(
// With this map operator we transform the given name to "Hello " + string
map((name) => `Hello ${name}`),
// With this map operator we add an exclamation mark after the nameWithGreeting
map((nameWithGreeting) => `${nameWithGreeting} !`)
);
The nameWithGreetingAndExclamation$ observable will output Hello Angular ! when subscribed to.
Using map() operator with HTTP
The map() operator can be used to transform data retrieved from APIs, as seen in this example. The API returns a list of users with both firstName and lastName properties. A fullName property is then assigned from the existing properties.
type User = {
firstName: string; // returned from API
lastName: string; // returned from API
fullName?: string; // fullName is not returned from API
};
@Component({
selector: 'my-app',
standalone: true,
imports: [CommonModule, ReactiveFormsModule, HttpClientModule],
template: `{{ users$ | async }}`,
})
export class App {
private readonly httpClient = inject(HttpClient);
public readonly users$: Observable<User> = this.httpClient
// API returns list of users with firstName and lastName
.get<User>('https://bryanhannes.com/api/users')
.pipe(
// Map to list of users which have the properties firstName, last and and fullName
map((user: User) => (
{
...user,
// fullName is equal to firstName + ' ' + lastName
fullName: `${user.firstName} ${user.lastName}`,
}
))
);
}
Using map() to transform an array
When using the map() to transform an array, we have to keep in mind that we are transforming the whole array, not the individual items in the array.
To work around this, the Array.map() function can be used inside the RxJS map() operator.
// Input
const names = [
'Alice',
'Bryan',
'John',
];
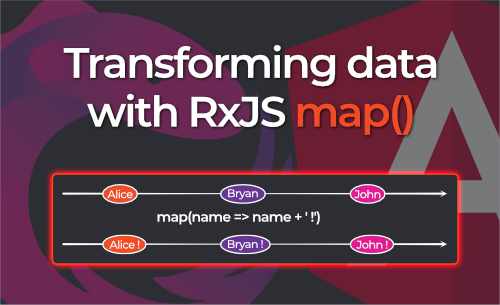
namesWithExclamation$: Observable<string[]> = of(names)
.pipe(
// Note that the map operator gets the whole array of name here
// and not the individual items of the array
map((names: string[]) => {
// We can use `Array.map()` to transform all the items in the array
return names.map((name) => `${name} !`);
})
);
// Output
'Alice !'
'Bryan !'
'John !'
Conclusion
- The
map()operator is a must-have for your RxJS tool belt. - It can be used to transform data from one type to another or adding/changing properties.
- When using
map()to transform an array, remember to use theArray.map()function inside the RxJSmap()operator.
Other articles you might like
-

Generating icon components from SVG files with NX and Angular
-

Angular + NGINX + Docker
-

How to Call the OpenAI API Directly from Angular (with streaming)
-

Custom TitleStrategy in Angular
-

RxJS catchError: error handling
-
RxJS distinctUntilChanged: filtering out duplicate emissions
-

RxJS combineLatest: how it works and how you can use it in Angular
-

Delaying streams with RxJS debounceTime
-
Real-life use cases for RxJS SwitchMap in Angular
-

Typesafe view models with RxJS and Angular
-

Reactively storing and retrieving URL state in Angular
-

Let's build an Image Generator with OpenAI and Angular
-
Why you should externalize your Angular Configuration
 Written by Bryan Hannes
Written by Bryan Hannes